Datawearhouse Architecture Overview
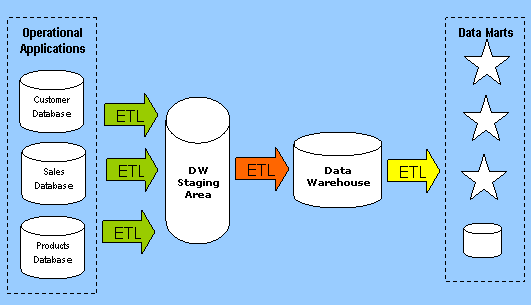
Architecture Overview:
Data Warehouses can be architected in many different ways, depending on the specific needs of a business. The model shown above is the "hub-and-spokes" Data Warehousing architecture that is popular in many organizations.Operational Systems
Operational Systems :

Architecture Overview:
Data Warehouses can be architected in many different ways, depending on the specific needs of a business. The model shown above is the "hub-and-spokes" Data Warehousing architecture that is popular in many organizations.Operational Systems
Operational Systems :
The principal reason why businesses need to create Data Warehouses is that their corporate data assets are fragmented across multiple, disparate applications systems, running on different technical platforms in different physical locations. This situation does not enable good decision making.
When data redundancy exists in multiple databases, data quality often deteriorates. Poor business intelligence results in poor strategic and tactical decision making.
Individual business units within an enterprise are designated as "owners" of operational applications and databases. These "organizational silos" sometimes don't understand the strategic importance of having well integrated, non-redundant corporate data. Consequently, they frequently purchase or build operational systems that do not integrate well with existing systems in the business.
Data Management issues have deteriorated in recent years as businesses deployed a parallel set of ebusiness and ecommerce applications that don't integrate with existing "full service" operational applications.
ETL Process :
ETL Technology (shown above with arrows) is an important component of the Data Warehousing Architecture. It is used to copy data from Operational Applications to the Data Warehouse Staging Area, from the DW Staging Area into the Data Warehouse and finally from the Data Warehouse into a set of conformed Data Marts that are accessible by decision makers.
Staging area:
The Data Warehouse Staging Area is temporary location where data from source systems is copied. A staging area is mainly required in a Data Warehousing Architecture for timing reasons. In short, all required data must be available before data can be integrated into the Data Warehouse.
Due to varying business cycles, data processing cycles, hardware and network resource limitations and geographical factors, it is not feasible to extract all the data from all Operational databases at exactly the same time.
Datawearhouse purpose:
The purpose of the Data Warehouse in the overall Data Warehousing Architecture is to integrate corporate data. It contains the "single version of truth" for the organization that has been carefully constructed from data stored in disparate internal and external operational databases.
The amount of data in the Data Warehouse is massive. Data is stored at a very granular level of detail. For example, every "sale" that has ever occurred in the organization is recorded and related to dimensions of interest. This allows data to be sliced and diced, summed and grouped in unimaginable ways.
Data Mart:
ETL (Extract Transform Load) jobs extract data from the Data Warehouse and populate one or more Data Marts for use by groups of decision makers in the organizations. The Data Marts can be Dimensional (Star Schemas) or relational, depending on how the information is to be used and what "front end" Data Warehousing Tools will be used to present the information.

This is a very good content I read this blog, please share more content on MSBI Online Training
ReplyDelete